read also
 Over €175 Million in Tax Refunds Remain Unclaimed in Greece
Over €175 Million in Tax Refunds Remain Unclaimed in Greece
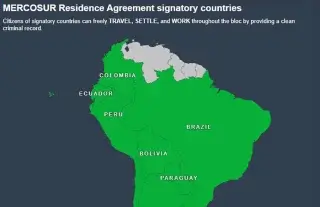 Citizenship in South America: How the Mercosur Agreement Works
Citizenship in South America: How the Mercosur Agreement Works
 Rising Crime Levels in Several Canadian Cities
Rising Crime Levels in Several Canadian Cities
 Türkiye strengthens its role in global tourism
Türkiye strengthens its role in global tourism
 Slovenia Work Permits Become a Key Hiring Bottleneck
Slovenia Work Permits Become a Key Hiring Bottleneck
 Asset Reinvention Reshapes Thailand’s Hotel Market
Asset Reinvention Reshapes Thailand’s Hotel Market
China Unveils New Economic Reform Program to Strengthen Domestic Market and Mitigate Challenges

China's National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) has published a comprehensive set of recommendations to bolster the nation’s economy, focusing on creating a unified domestic market and reducing regional protectionism. The action plan, announced in early 2025, addresses key areas such as property rights protection, fair competition, and regulatory reforms spanning transportation, telecommunications, land trade, and product standards, according to a Bloomberg report.
Key Goals of the New Plan
The reforms aim to enhance domestic demand, which Beijing has identified as a top priority for sustaining economic growth amidst the looming threat of U.S. tariffs on Chinese exports. According to NDRC official Wang Shancheng, the guidelines provide a roadmap for regional integration into a single, cohesive national market. Wang emphasized that this unified market would be open to all participants, fostering a level playing field for businesses and investors alike.
Highlights of the proposed reforms include:
Streamlining market access rules: Ensuring consistent standards across regions to eliminate barriers that hinder investments in specific sectors.
Improving connectivity: Enhancing transportation networks between regions to reduce logistics costs.
Addressing administrative inefficiencies: Cutting excessive local government fees imposed on businesses and standardizing local regulations for data trade, product quality, and administrative governance.
Boosting Efficiency and Competitiveness
Wang underlined the significance of these reforms in leveraging China’s vast market potential. The unified market is expected to consolidate resources, drive innovation, modernize industries, and stimulate economic growth, providing resilience against global uncertainties.
Key measures include:
Introducing a market conduct code to regulate excessive administrative fines imposed by local officials.
Removing residency restrictions that prevent migrant workers from accessing social benefits in cities where they work.
Integrating housing and healthcare insurance systems across regions, enabling contributions and withdrawals regardless of location.
Expert Opinions and Challenges
International analysts have responded cautiously to the reforms, noting positive developments but also highlighting persistent challenges. For instance, China’s struggling real estate sector remains a critical focus area. After years of decline, real estate sales in December 2024 stabilized compared to the same period in 2023. However, prices have been falling for three consecutive years, and banks recently raised mortgage rates for new borrowers.
Outlook for the Real Estate Sector:
Analysts at Morgan Stanley predict increased market consolidation in 2025, as private developers prioritize project completions and debt reduction. This could present growth opportunities for state-owned developers.
Morningstar analyst Jeff Zhang anticipates price stabilization in the second half of 2025, driven by the financial health of state-backed developers.
Fitch Ratings forecasts a 10% decline in new home sales and a 5% drop in prices in 2025, though the pace of decline is expected to slow.
Economic Projections for 2025
China's GDP growth for 2024 was estimated at 4.9%, supported by government stimulus measures and robust exports, according to a Reuters survey of 64 economists. However, the forecast for 2025 suggests a slowdown to 4.5%, with further deceleration to 4.2% in 2026. Contributing factors include:
The introduction of higher tariffs on Chinese goods by U.S. President Donald Trump.
A decline in real estate activity and reduced consumer spending.
The People's Bank of China is expected to lower the reserve requirement ratio (RRR) for banks by at least 25 basis points in the first quarter of 2025, following two reductions in 2024. Inflation is projected to rise from 0.2% in 2024 to 0.8% in 2025, continuing upward to 1.4% by 2026.
China’s latest economic reform agenda is a bold attempt to unify its domestic market, streamline regulations, and enhance its global competitiveness. While the proposed measures reflect the government’s commitment to addressing structural inefficiencies, their effectiveness will depend on consistent implementation and the ability to navigate geopolitical and economic challenges. As China adapts to a rapidly evolving global landscape, its success in sustaining growth and stability will have far-reaching implications for the global economy.


