Home Sales in the U.S. Begin to Rise

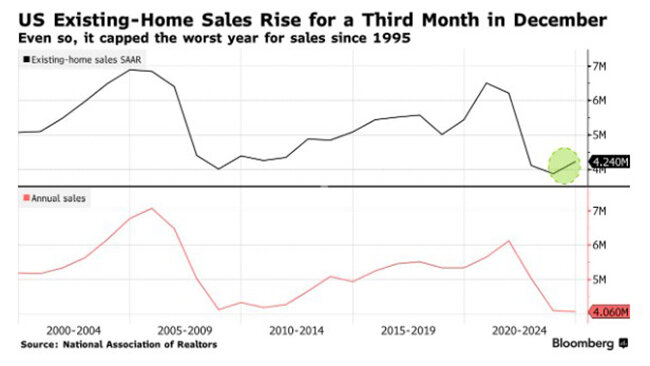
The U.S. housing market saw one of its worst years in decades in 2024. Existing home sales fell to their lowest level since 1995. However, in recent months, the market has shown signs of recovery, according to Bloomberg, citing data from the National Association of Realtors (NAR). Analysts remain cautious about calling it a full stabilization due to persisting economic risks.
For three consecutive years, home sales have declined, a trend previously seen only during recessions in the 1980s, 1990s, and during the 2006 housing crisis. Experts cite high mortgage rates in 2024 as the main obstacle. In early January 2025, the 30-year fixed mortgage rate stood at 6.91%. Meanwhile, the median home price increased by 6% in 2024, reaching $404,400, further impacting housing affordability.
Market Adjustments and Growing Sales
Despite these challenges, experts believe homeowners and buyers have adjusted to mortgage rates hovering around 7%. This is supported by a 2.2% increase in existing home sales in December, bringing the annualized rate to 4.24 million transactions.
53% of homes were on the market for less than a month, similar to November figures.
16% of properties were sold above the asking price.
New home sales also showed signs of stabilization, reinforcing cautious optimism.
Overall, sales were up 10.8% year-over-year on an unadjusted basis.
Regional and Investment Trends
Home sales increased in three out of four U.S. regions, with the Northeast seeing a nearly 4% rise.
Single-family home sales grew by 1.9%.
Sales of multi-owner and co-op housing units reached their highest levels since February.
Investors and second-home buyers accounted for 16% of transactions, up from 13% in November.
All-cash purchases made up 28% of sales, while 31% of buyers were first-time homebuyers.
Economic Context and Consumer Spending
Consumer spending in the U.S. rose by nearly 4% over 12 months, adjusting for inflation.
There was hope that 2024 could be a turning point, as the Federal Reserve had begun cutting interest rates.
However, mortgage rates continued rising, and inflation remained high, raising concerns that policymakers had eased monetary policy too soon.
Household bank balances remained strong due to stimulus payments issued during the pandemic, which could positively impact the economy in 2025.
Mortgage Debt and Financial Pressures
According to Bloomberg, Americans are paying down more of their credit card debt, despite interest rates nearing record highs.
The share of borrowers making only minimum payments reached the highest level ever recorded in 2024.
Mortgage rates are expected to remain above 6% for the next few years, adding continued pressure on affordability.
Challenges and Future Outlook
“The outlook for 2025 is slightly better, but still challenging, as the triple threat of high mortgage rates, rising home prices, and limited supply will persist,” noted Robert Frick, corporate economist at Navy Federal Credit Union.
Wages are growing faster than inflation, but housing and commercial construction activity has slowed.
Spending on capital construction has declined, though investments in data centers and semiconductor factories have offset some losses.
Exports remained stable, while imports increased, driven by the strong U.S. dollar, making American-made goods more expensive abroad.
Geopolitical and Trade Risks
The U.S. housing market could also be affected by new U.S. tariff policies and retaliatory tariffs from trading partners.
Experts warn that while a full-scale global trade war is unlikely to cause a recession, it may slow economic growth.
GDP is projected to slow to 2.1% in 2025 and 1.6% by the end of 2026, with AI-driven productivity improvements being the main factor that could counterbalance the decline.
While the housing market is showing early signs of recovery, its long-term outlook remains uncertain, heavily dependent on mortgage rates, inflation trends, and government policies.








