read also
 Japan Corporate Bankruptcies Hit 13-Year High
Japan Corporate Bankruptcies Hit 13-Year High
 Japan’s New Condo Prices Reach Record High
Japan’s New Condo Prices Reach Record High
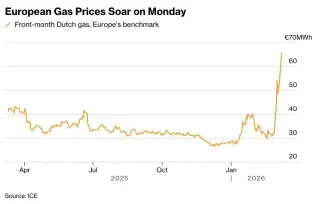 European Gas Prices Surge Amid Middle East War
European Gas Prices Surge Amid Middle East War
 EU prepares new foreign investment screening rules
EU prepares new foreign investment screening rules
 Collapse of Air Travel in the Middle East
Collapse of Air Travel in the Middle East
 New research highlights rising hotel tax compliance costs in the United States
New research highlights rising hotel tax compliance costs in the United States
TOP-10 Richest Countries in the World
In 2025, the gap between the global wealth leaders reached its highest level in the past decade. The difference between the first and the tenth country in the ranking exceeds $100,000 per capita, reported the Get Golden Visa platform. The United States, China, and Germany traditionally occupy the top positions by total economic output, while Luxembourg leads in GDP per capita.
The study takes into account the overall scale of the economy and the population’s well-being, which helps assess the quality of life in each country. A broader picture is provided by additional indicators such as the Human Development Index, purchasing power parity, the World Bank’s calculations of total national wealth, as well as investment levels, support for entrepreneurs, and the ability to attract foreign capital.
1. Luxembourg

According to the International Monetary Fund, Luxembourg remains the richest country in the world with a GDP per capita of $141,080 and a population of fewer than 700,000 people. Its economy relies on a highly developed financial sector, banking services, logistics, steel production, IT, and space technologies, ensuring resilience and a stable inflow of capital.
Its strategic location in the heart of Europe further strengthens its advantages. After Brexit, Luxembourg became a convenient base for European headquarters and international companies needing access to EU markets. Interest is also supported by its residency-by-investment program: a three-year residence permit is available with an investment starting from €500,000, subject to verified income, a clean criminal record, and health insurance.
2. Singapore

Singapore ranks second among the world’s richest countries, with a GDP per capita of $93,956 and a population of around 6 million. Its economic model is built on long-term planning and active attraction of foreign capital. High-net-worth individuals may obtain permanent residency by investing at least 10 million Singapore dollars, and after two years of residence, they may apply for citizenship.
The country also stands out for its high level of digitalization, accounting for about 17% of the economy. The government promotes technological initiatives such as Smart Nation to support innovation and introduce digital solutions across key sectors. This approach strengthens Singapore’s position among the global leaders in wealth and economic competitiveness.
3. United States

The United States has a GDP per capita of $89,678 and a population of about 340 million. Its economy remains the largest in the world thanks to resilience, diversification, and high productivity. The country possesses substantial oil and gas reserves, which added $257 billion to GDP in 2023. High-tech industries, financial services, insurance, and real estate also play a crucial role. Investment in education amounts to 5.6% of GDP, exceeding the OECD average.
The U.S. actively encourages entrepreneurship: in 2025, around 430,000 new business applications were submitted each month, highlighting the importance of small businesses for the national economy. Foreign investors may apply for the E-2 Treaty Investor Visa, available to citizens of treaty countries and requiring investment in a real operating business in the U.S. This approach supports a favorable business climate and stimulates capital inflows.
4. Qatar

Qatar’s GDP per capita stands at $72,760. The country’s economy heavily depends on the extraction and export of hydrocarbons: according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, in 2021 this sector accounted for 81% of total revenue, amounting to $77 billion. Qatar remains one of the world’s largest LNG suppliers, forming the foundation of its national wealth.
At the same time, Qatar is expanding into financial services, tourism, and information technologies, gradually reducing dependence on gas. In 2020, the country launched a residency-by-investment program: temporary residence is granted for property purchases starting at $200,000, while permanent residency requires an investment of $1 million. Applicants must spend at least 90 days per year in the country. This strategy diversifies the economy and increases its resilience.
5. Germany

Germany has a GDP per capita of $57,914 and remains Europe’s largest economy. In 2023, its nominal GDP reached $4.5 trillion, providing a high standard of living, a stable labor market, and a developed social support system. Key sectors include industry, services, and technology. Germany remains Europe’s leading manufacturing hub: in 2024, the industrial sector generated 19.7% of GDP and produced €2.9 trillion in output.
High average incomes make the country attractive to skilled professionals and entrepreneurs. While Germany does not offer a classic Golden Visa, foreign investors may obtain residency by establishing a business that meets the requirements of the investment program. High-quality infrastructure, healthcare, and education help maintain Germany’s strong global economic position.
6. Hong Kong

Hong Kong is one of the world’s most dynamic economies, with a GDP per capita of $55,608 and a population exceeding 7.5 million. In 2023, its nominal GDP reached about $380 billion. The region’s economy is oriented toward services, which account for over 16% of total output, including finance, logistics, trade, tourism, and professional services. Hong Kong plays a significant role in global trade and remains a major financial center in Asia.
Development plans include further diversification and the promotion of innovation. Investors may obtain residency through the Capital Investment Entrant Scheme (CIES) and its updated version, which require investment in approved assets. These programs help maintain Hong Kong’s attractiveness to international businesses and expatriates.
7. United Kingdom

The United Kingdom has a GDP per capita of $54,280 and remains one of the world’s wealthiest nations. About 80% of its economy is generated by the services sector, including finance and insurance, while industry and construction account for another 16%. Despite the consequences of Brexit and global pressures, the economy posted moderate growth at the beginning of 2025, ranging from 0.3% to 0.7% per quarter.
The country continues to attract international businesses thanks to its developed financial system, strong legal framework, and access to global markets. Entrepreneurs may apply for the Innovator Founder Visa, which enables the establishment or expansion of a business in the UK. This supports capital inflows and investor interest.
8. UAE

The United Arab Emirates ranks among the wealthiest countries in the Middle East with a GDP per capita of $51,294. The economy relies heavily on oil and gas: about 30% of GDP comes from hydrocarbon extraction and exports, while external trade accounts for another 13%. Alongside this, the UAE is expanding tourism, finance, logistics, and technology to build a more sustainable growth model.
The country offers favorable business conditions: no income tax, a 9% corporate tax for companies earning over 375,000 dirhams, and additional benefits in free economic zones. Its Golden Visa program also stimulates investor interest: a two-year residency is available with a property purchase from $204,000, and a ten-year visa requires at least $545,000.
UAE Introduces a 10-Year “Golden Visa” for Philanthropists
9. Italy

Italy’s GDP per capita is $41,714, with a nominal GDP of about $2.37 trillion. Its economy relies on manufacturing, fashion, the automotive industry, and tourism. Despite high public debt — over 135% of GDP — and sluggish productivity growth, the economy remains stable. Challenges include youth unemployment and an aging population, which increase pressure on social systems.
Nevertheless, Italy remains attractive to investors. The country offers residency through investment: from $250,000 into startups or from €500,000 into a company. This supports capital inflows and strengthens key sectors.
10. Japan

Japan ranks among the world’s wealthiest nations with a GDP per capita of $35,611 and a population of around 124 million. Its economy is based on industry and high-tech production, but the country depends on imported resources and faces rising public debt and a shrinking workforce due to population aging. In 2025, the trade balance was negative: in August, the deficit reached 242.5 billion yen.
To stimulate growth, Japan is implementing reforms aimed at encouraging investment and business development. Foreign nationals may obtain an Investor/Manager Visa by investing at least ¥5 million ($34,000), maintaining a physical office, and hiring at least two full-time employees. The visa is issued for 1–5 years and can be renewed.
Conclusion
Analysts at International Investment note that the global distribution of wealth in 2025 reflects the lasting advantage of countries combining technological development, stable institutions, strong infrastructure, and strategic capital management. The leaders maintain their positions not only because of economic size but also due to their ability to adapt to global shifts, attract investment, and support innovation. Countries that focus on increasing efficiency and expanding economic opportunities continue to strengthen their competitiveness and build long-term growth potential.



